5. Enumeration
Jan 27, 2021
Measuring Efficiency
- for sequential computation time == work
- in parallel computation time \(\neq\) work
Example
| P | T | W |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 50 | 100 |
| 3 | 40 | 120 |
| 4 | 30 | 120 |
Whether time or work is better, depends on the criteria.
Summation Tree to Array
Consider binary tree / array representation of A:
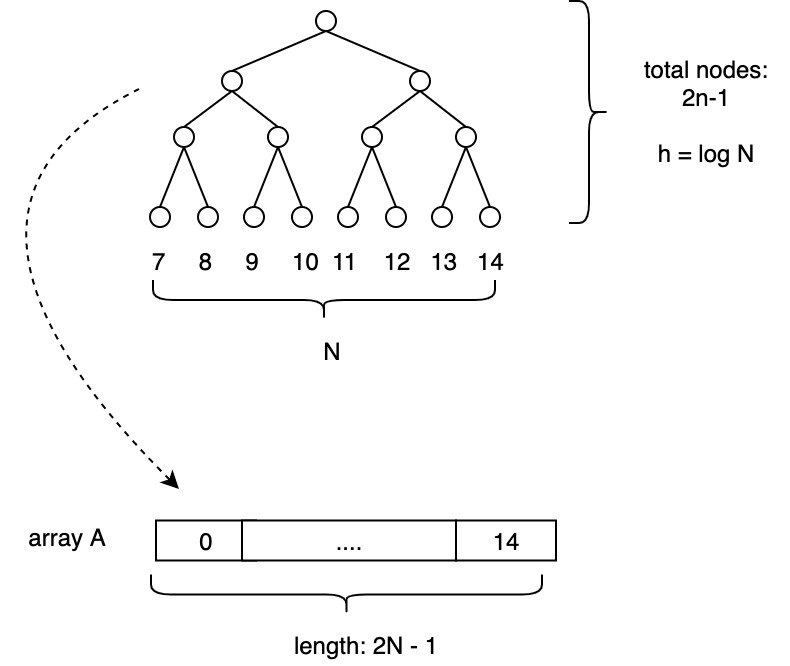
Assign \(N\) processors (\(P_{N-1} \dots P_{2N-1}\)) to leaf nodes
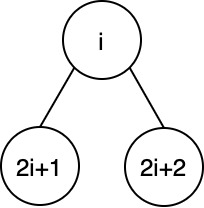
For any non-leaf node \(i\): \(A[i] = A[2i + 1] + A[2i + 2]\) where: - \(A[2i + 1]\) is its left child - \(A[2i + 2]\) is its right child
Or use parity: if child == 2 * parent + 1 then left child else right child (knowing this is important in CREW PRAM model)
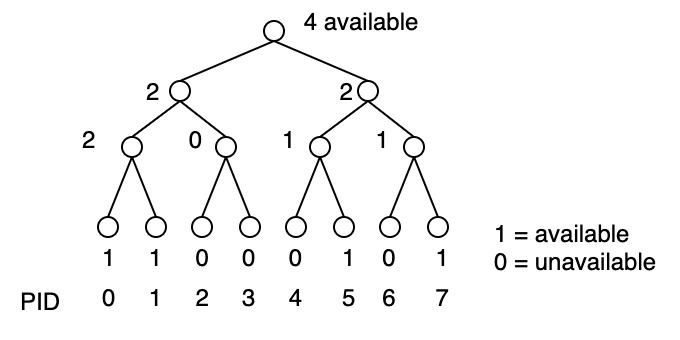
Processor Enumeration
Find out how many processors are available for use. Iterate bottom to top:
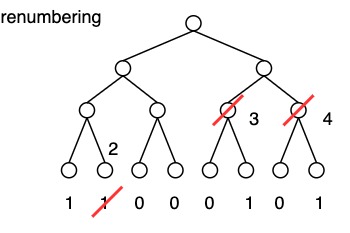
After finding available processors renumber them by looking at left neighbor then increment. Repeat at each tree height. After this pass processors have renumbered themselves.
| Processor enumeration, bounds |
|---|
| \(T_1^* = \Theta(P)\) |
| \(T_P = \Theta(\lg P)\) |
| \(W = P \cdot T_P = \Theta(P \lg P) = O(T_1 \cdot \lg P)\) |
This is log-efficient
-
callocis C command used to clear and allocate memory (related tomalloc);- it writes 0 to allocated memory space
- solves the issue when counting 0s and there are inactive processors → clears beofre use
- Recall in PRAM, memory is initialized to 0s
-
If processor enumeration fails (dynamic failures) enumeration ends with an overestimate
- this is not a huge issue; other processors can pick up the work
- overestimate is bad as it leads to redundant work and kills efficiency
- (obviously) aim at exact number when enumerating but if unable to get exact number, overestimate is better than underestimate
- Runtime failures may cause overestimates
Ternary and higher degree trees
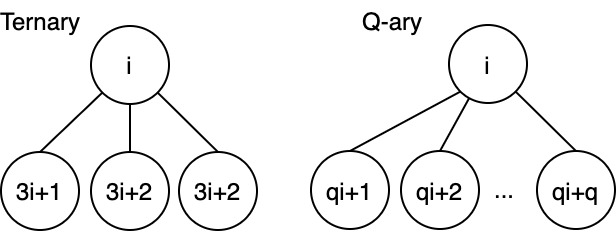
Ternary tree has degree 3 - tree height is \(\lg_{3}N\) - non-leaf node \(i\) has 3 children: - left child at \(3i + 1\) - middle child at \(3i + 2\) - right child at \(3i + 3\)
In general, for any Q-ary tree: - tree height is \(\lg_{q}N\) - children - left child \(qi + 1\) - next child \(qi + 2\) - ... - last child \(qi + q\)