20. HW architectures
Mar 22, 2021
Symmetric multiprocessing
Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware and software architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single, shared main memory, have full access to all input and output devices, and are controlled by a single operating system instance that treats all processors equally, reserving none for special purposes. Most multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture.

Crossbar architecture
In 1970s: IBM built mainframe computers realizing it is a bottleneck → how to improve? Crossbar architecture with switch at each intersection.
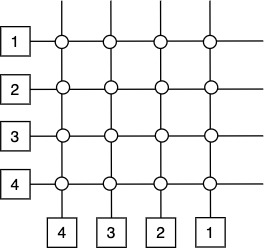
- uses source routing to navigate and to exchange data
- 4 processors can access 4 banks of data concurrently
- this system does not scale well due to hardware cost
Hardware cost of crossbar:
\(HW\$ = c_1 \cdot P + c_2 \cdot \text{Memory} + c_3 \cdot \Omega(P^2)\)
Hardware cost for parallel:
\(HW\$ = c_1 \cdot P + c_2 \cdot \text{Memory} + c_3 \cdot \text{wire} = \Theta(P)\)
Another idea: cut crossbars by half

\(HW\$ = c_1 \cdot P + c_2 \cdot \text{Memory} + c_3 \cdot \Omega(\frac{P^2}{2})\)
Asymptotically not better but from a practical standpoint this is a significant saving.
Linear processor array
Next suggestion: make a linear processor array (also called systolic array).
\(HW\$ = c_1 \cdot P + c_2 \cdot \text{Memory} + c_3 \cdot \text{Wires}\)

Assume we have a PRAM \(P=N\), \(W = P \cdot T_P\). Simulate sequential processor doing DO-ALL. How does P get data from 1? Need:
- \(P-1\) steps to read
- 1 step to compute, and
- \(P-1\) steps to write
Simulation time: \(T = (P-1 \cdot T_P)\)
Simulation work: \(W = \Theta(P^2) \cdot T_P\)
This is not a good algorithm for this architecture, but the algorithm itself is still good. This architecture may be suitable from specialized problems, not for general purpose problems. One suitable application is zero-time sorter.